I. Introduction
Centrifugal pumps play a vital role in industrial production. They are widely used in numerous industries such as chemical, petroleum, pharmaceutical, electric power, and metallurgy, serving as the key equipment for fluid transportation. In industrial production lines, centrifugal pumps can ensure the continuity and stability of the technological process, providing a continuous supply of liquid or gas for many production links. Their highly efficient transportation capabilities, enabling the conveyance of a large amount of media with relatively low energy consumption, are of great significance for improving industrial production efficiency and reducing costs. Moreover, in some special environments, centrifugal pumps can effectively prevent leakage and pollution through the selection of sealing structures and materials, thus ensuring production safety.
Given the indispensability of centrifugal pumps in industrial production, it is particularly necessary to explore the factors that affect the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps. Only by having a in-depth understanding of these factors can we better optimize the performance of centrifugal pumps and improve their working efficiency, thereby bringing greater benefits to industrial production.
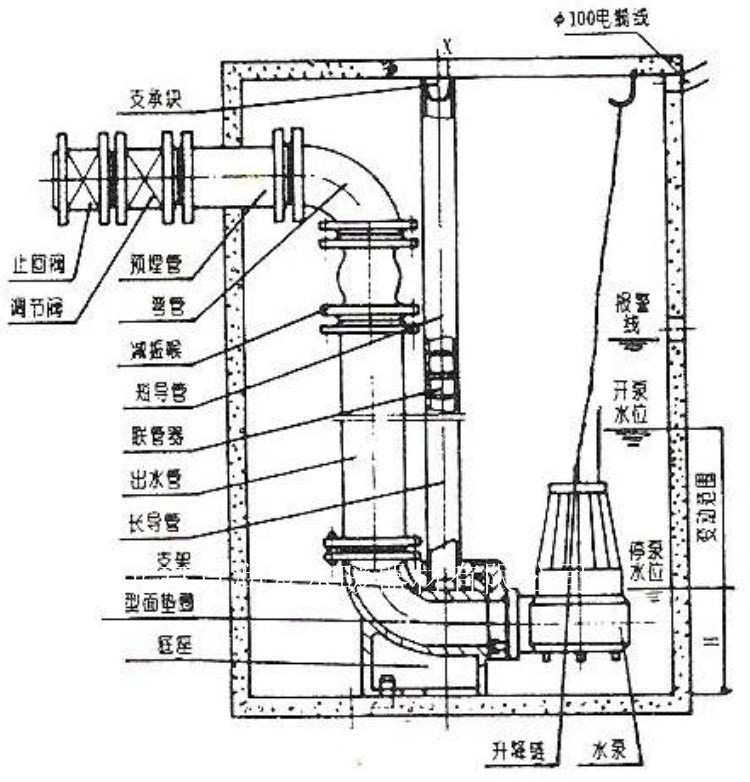
II. Factors Affecting the Working Efficiency of Centrifugal Pumps
(I) Pump Efficiency Itself
Among the many factors affecting the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps, the efficiency of the pump itself plays a fundamental role. Under the same working conditions, the efficiencies of different centrifugal pumps may vary by more than 15%. This is because different pumps differ in aspects such as design, manufacturing process, and material selection. Some high-quality centrifugal pumps are more reasonably designed and can better adapt to the working environment, thus improving the working efficiency. However, some low-quality pumps may have problems such as unreasonable structures and non-durable materials, resulting in low efficiency.
(II) Operating Conditions
The operating conditions of centrifugal pumps also have a significant impact on their working efficiency. When the operating conditions of a centrifugal pump are below the rated conditions, the pump efficiency will decrease and the energy consumption will be high. This is because when operating below the rated conditions, the parameters such as flow rate and head of the pump cannot reach the optimal state, thus leading to a decline in efficiency. For example, in actual production, if the flow rate demand of a centrifugal pump is less than the rated flow rate, the pump may operate in a low-efficiency area, wasting energy.
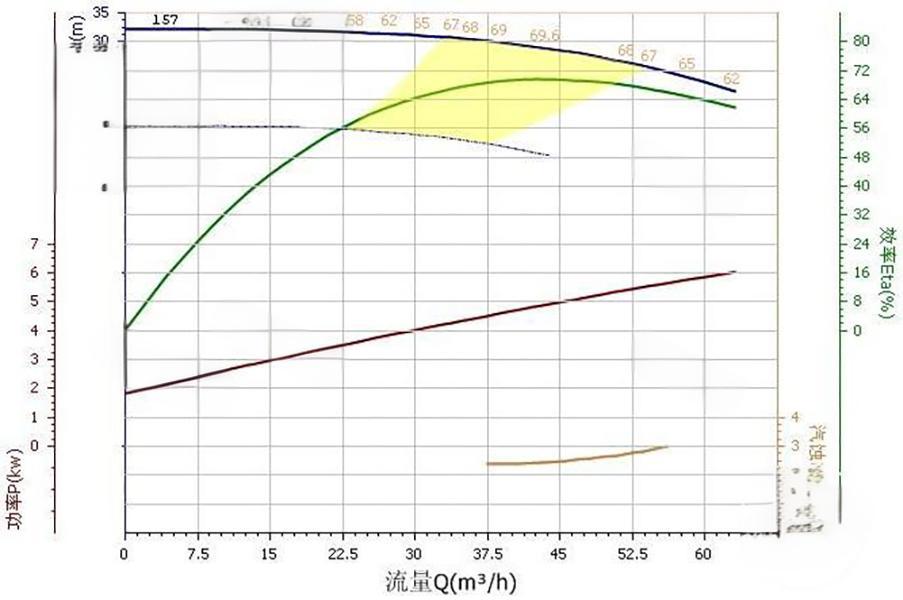
(III) Motor Efficiency
The motor efficiency basically remains unchanged during operation. Therefore, it is crucial to select a high-efficiency motor. A high-efficiency motor can provide stable power for the centrifugal pump, thereby improving the efficiency of the entire pump unit. If the motor efficiency is low, even if the centrifugal pump itself has a high efficiency, the working efficiency will also be affected due to insufficient power.
(IV) Mechanical Efficiency
Mechanical efficiency is mainly related to the quality of design and manufacturing. After the pump is selected, the impact of subsequent management on mechanical efficiency is relatively small. High-quality design and manufacturing can ensure close cooperation between the various components of the centrifugal pump, reducing mechanical friction losses and improving mechanical efficiency. However, if there are defects in the design or manufacturing, it may lead to an increase in friction between the components, reducing the mechanical efficiency.
(V) Hydraulic Losses
Hydraulic losses include hydraulic friction and local resistance losses. With the increase in the running time of the centrifugal pump, the surfaces of components such as impellers and guide vanes will gradually wear, which will lead to a decrease in hydraulic efficiency. For example, the wear on the surface of the impeller will cause more vortices and resistance in the liquid flow process, thereby increasing hydraulic losses. In addition, local resistance losses will also increase with the unreasonable layout of the pipeline.
(VI) Volumetric Losses
Volumetric losses, also known as leakage losses, are related to design, manufacturing, and subsequent management. During the operation of the centrifugal pump, the friction between components will cause the gaps to increase, thereby reducing the volumetric efficiency. For example, the increase in the gaps in areas such as the impeller seal ring, between stages, and the axial force balance mechanism will increase the liquid leakage, reduce the output flow of the pump, and further affect the working efficiency.
(VII) Other Factors
In addition to the above factors, there are also some other factors that can affect the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps. For example, the blockage of the filter tank and the entry of air into the pipeline will cause cavitation and idling. Insufficient preparation work before starting will cause the cavitation phenomenon, reducing the pump efficiency. The blockage of the filter tank will lead to a decrease in the liquid flow rate, increasing the load on the pump and reducing the efficiency. The entry of air into the pipeline will cause bubbles to form in the pump, affecting the normal transportation of the liquid and even causing the pump to fail to work. If the basic operating procedures such as warming the pump, turning the pump by hand, and priming the pump are not thoroughly executed before starting, the cavitation phenomenon will occur when the pump is started, causing the pump to produce loud noise and severe vibration, reducing the pump efficiency.
III. Strategies for Improving the Working Efficiency of Centrifugal Pumps
(I) Selecting Appropriate Centrifugal Pumps
Select centrifugal pumps whose parameters are close to the actual operating conditions to ensure operation in a high-efficiency state.
When selecting a centrifugal pump, the actual operating conditions should be fully considered to ensure that the parameters of the selected pump match the actual requirements. For example, according to the required flow rate, head, and other parameters, referring to the types and selection principles of centrifugal pumps, select from different types such as single-stage centrifugal pumps, multi-stage centrifugal pumps, vertical centrifugal pumps, and submersible centrifugal pumps. If the flow rate demand is large and the head requirement is not high, a single-stage centrifugal pump can be selected; if high heat and high-pressure transportation are required, a multi-stage centrifugal pump is more appropriate. At the same time, the appropriate pump material should be selected according to the characteristics of the liquid. For example, corrosion-resistant materials should be selected for corrosive liquids to ensure the pump's long-term stability.
(II) Applying Energy-saving Technologies
The frequency conversion energy-saving technology can make the pump always operate in the high-efficiency area.
The frequency conversion speed regulation technology is one of the important means to improve the efficiency of centrifugal pumps. By adjusting the frequency of the motor, the rotational speed of the pump can be changed according to the actual operating conditions, enabling the pump to maintain high-efficiency operation under different loads. For example, when the production load decreases, the rotational speed of the motor is reduced, thereby reducing the flow rate and head of the pump, avoiding energy waste under low loads. For centrifugal pumps whose design parameters are greater than the actual operating conditions, after installing the frequency conversion speed regulation device, they can always operate in the high-efficiency area, effectively improving the energy utilization efficiency.
Promote the application of new energy-saving products such as permanent magnet speed regulation motors and dual-power motors.
New energy-saving motors such as permanent magnet speed regulation motors and dual-power motors have higher efficiency and stability. They can provide more reliable power for centrifugal pumps and reduce energy losses. Promoting the application of these new energy-saving products on major centrifugal pumps can significantly improve the efficiency of the entire pump unit and reduce running costs.
(III) Strictly Following Operating Procedures
Before starting, do a good job of turning the pump by hand, priming the pump, and other preparation work to prevent the cavitation phenomenon.
Strictly follow the operating procedures of the centrifugal pump. Before starting, turn the pump by hand, open the inlet valve, close the outlet valve perform exhaust and venting operations, and check whether the inlet pressure of the pump meets the requirements. This can effectively prevent the cavitation phenomenon caused by low supply liquid pressure and insufficient flow rate. Cavitation will cause the pump to produce loud noise and severe vibration, reducing the pump's efficiency. Therefore, doing a good job of preparation work before starting is crucial.
Regularly clean the filter tank to ensure the smoothness of the inlet liquid pipeline.
Regularly clean the filter tank and check the pipeline connections to avoid problems such as filter tank blockage and pipeline air entry. The blockage of the filter tank will lead to a decrease in the liquid flow rate, increasing the load on the pump and reducing the efficiency; the entry of air into the pipeline will cause bubbles to form in the pump, affecting the normal transportation of the liquid. Ensuring the smoothness of the inlet liquid pipeline can ensure the stable operation of the centrifugal pump and improve the working efficiency.
(IV) Regularly Conducting Detection and Maintenance
Regularly conduct pump efficiency detection on centrifugal pumps and promptly find out the reasons and solve the problems.
Regularly conduct pump efficiency detection on centrifugal pumps to be able to promptly discover the problem of pump efficiency decline. When the pump efficiency decreases, the reasons should be promptly found out. It may be due to the wear of components such as impellers and guide vanes, resulting in an increase in hydraulic losses, or the increase in the gaps between components, causing an increase in volumetric losses. Corresponding measures should be taken for different problems, such as repairing or replacing the worn components, adjusting the gaps, etc., to restore the high-efficiency operation of the pump.
IV. Conclusion
The working efficiency of centrifugal pumps is affected by multiple factors. Through the analysis of these factors and the adoption of corresponding improvement strategies, the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps can be effectively improved, ensuring that they play a greater role in industrial production.
The factors affecting the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps mainly include pump efficiency itself, operating conditions, motor efficiency, mechanical efficiency, hydraulic losses, volumetric losses and other factors. In actual application, it is necessary to comprehensively consider these factors and adopt scientific management and maintenance measures to improve the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps.
To improve the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps, the following strategies can be adopted:
Selecting appropriate centrifugal pumps: Select centrifugal pumps whose parameters are close to the actual operating conditions to ensure operation in a high-efficiency state. At the same time, select the appropriate pump material according to the characteristics of the liquid.
Applying energy-saving technologies: Adopt frequency conversion energy-saving technology to make the pump always operate in the high-efficiency area. Promote the application of new energy-saving products such as permanent magnet speed regulation motors and dual-power motors.
Strictly following operating procedures: Before starting, do a good job of turning the pump by hand, priming the pump, and doing other preparation work to prevent the cavitation phenomenon. Regularly clean the filter tank to ensure the smoothness of the inlet liquid pipeline.
Regularly conducting detection and maintenance: Regularly conduct pump efficiency detection on centrifugal pumps and promptly find out the reasons and solve the problems.
It is of great importance to conduct scientific management and maintenance of centrifugal pumps. This not only can improve the working efficiency of centrifugal pumps, and reduce energy consumption, but also can extend the service life of centrifugal pumps, reduce equipment maintenance costs, and bring greater benefits to industrial production. In actual operation, it is necessary to strictly follow the operating procedures, regularly conduct detection and maintenance, promptly discover and solve problems, and ensure that the centrifugal pump is always in a good working state.






















